Plate Tectonics
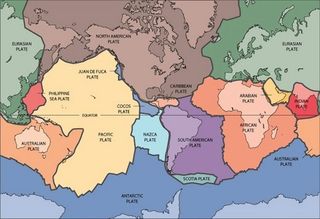
Plate tectonics is relatively new, put forth in the last 30 years or so — its forerunner was the now-discarded continental drift theory. The theory states that Earth's outer shell is made up of huge slabs of rock called plates that glide over the planet's inner layer, or mantle. As these plates shift, they sometimes collide with other plates, making for some interesting, and even deadly, results on Earth's surface, from erupting volcanoes, to earthquakes, to new mountain ranges. Here's a look at Live Science's news and features related to this constantly moving jigsaw puzzle.
Latest about plate tectonics

When was the last time Antarctica was ice-free?
By Victoria Atkinson published
Antarctica is covered by a miles-thick ice sheet, but was that always the case? And when was the coldest continent ice-free?

Mesmerizing animation shows Earth's tectonic plates moving from 1.8 billion years ago to today
By Alan Collins published
It's the first time Earth's geologic record — information found inside rocks — has been used to create an animation of this kind.

'Failed' microcontinent found hiding beneath Greenland and Canada
By Stephanie Pappas published
The Davis Strait, west of Greenland, holds a long-lost chunk of an almost-continent that didn't quite form about 58 million years ago.

Earth's plate tectonics fired up hundreds of millions of years earlier than we thought, ancient crystals reveal
By Stephanie Pappas published
New research hints that plate tectonics began earlier than 4 billion years ago — not long after Earth had formed.

Argyle mine: Earth's treasure trove of pink diamonds born during a supercontinent's break up
By Sascha Pare published
During 37 years of operations, the now-closed Argyle mine produced more than 865 million carats (191 tons) of rough diamonds and 90% of the world's pink diamonds.

50 interesting facts about Earth
By Stephanie Pappas, Robert Roy Britt, Ailsa Harvey last updated
Reference We've collected some of the most interesting and amazing facts about Earth

Weird blobs lurking near Earth's core may have been dragged from the surface
By Stephanie Pappas published
A new study of seismic data from Antarctica finds that the mantle may be stranger and more variable than previously believed, with pieces of ancient crust that have been dragged down by tectonic forces.
Mass die-off half a billion years ago caused by shifting tectonic plates, ancient rocks reveal
By Stephanie Pappas published
A large extinction in the midst of the expansion of life during the Cambrian period was caused by the tectonics of a supercontinent, new research argues.
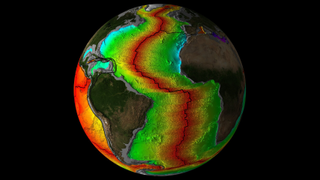
Sleeping subduction zone could awaken and form a new 'Ring of Fire' that swallows the Atlantic Ocean
By Sascha Pare published
A modeling study suggests a slumbering subduction zone below the Gibraltar Strait is active and could break into the Atlantic Ocean in 20 million years' time, giving birth to an Atlantic "Ring of Fire."
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.

